Clustering of symptoms of intracranial pressure time series for estimation of alarm function in traumatic brain injuries
Investigators: M. Teplan, I. Bajla, R. Rosipal)
When monitoring patients with severe head injury, the so-called method is used in clinical practice. critical value of the intracranial pressure time course (VLT). Exceeding this threshold is evaluated as an alarm situation, on the basis of which the medical staff initiates an emergency procedure (protocol) to save the patient’s life. However, much richer information is hidden in the archived VLT records of many monitored patients. Based on the known VLT curves for surviving and non-surviving patients, we proposed a new approach to monitoring the condition of hospitalized patients, which retrospectively takes into account the behavior of VLT time records of both these types of patients. For VLT time series, we designed several global and local flags that formed flag vectors in n-dimensional vector space. Using the hierarchical Gaussian mixed n-dimensional model approach, we proposed clustering of this space. Based on the a posteriori probabilities of clusters, three new alarm functions were proposed, the optimal thresholds of which we sought using the ROC (Receiver Operating Characteristic) approach and a new degree of efficiency. Cross-validation has shown the potential of new alarm functions as a useful complementary tool to the basic VLT critical threshold method.
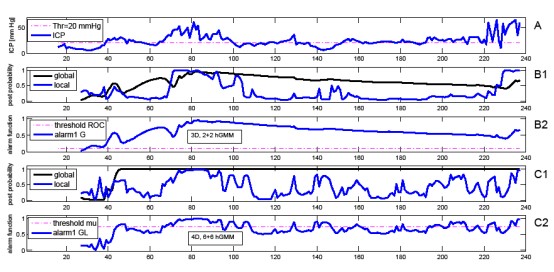
Fig. 1: Example of optimal VLT alarm function waveforms (duration – 240 hours) for a fatal patient calculated from a retrospective set of 45 VLT records: A-basic record with conventional VLT threshold, B1 and C1-global and local a posteriori probability waveforms for different hGMM models, B2 -alarm1G with its threshold, C2- alarm1GL with its threshold.
Cooperation with TU Vienna (Prof. Dr Med. Walter Mauritz) and Trnava University (Prof. I. Rusnák).
Related projects:
• VEGA 2/0043/13, VEGA 2/0138/16, VEGA 2/0011/16, MZ 2013/56-SAV-6, APVV-0668-12, APVV-14-0875.
Publications:
- TEPLAN, M. – BAJLA, I. – ROSIPAL, R. – RUSNÁK, M.: Feature clustering of intracranial pressure time series for alarm function estimation in traumatic brain injury. Physiological Measurement, 2017, 38, s.2015– (CC časopis, IF=2,058).
- TEPLAN, Michal – BAJLA, I. – ROSIPAL, R. – RUSNÁK, M.: Feature clustering of intracranial pressure time series for alarm function estimation in traumatic brain injury. Electronic supplement http://iopscience.iop.org/0967-3334/38/11/2015/media/aa8a51_Teplan_Supp.pdf
- BAJLA, I. – ŠKOVIERA, R. – TEPLAN, M.: An alternative of the sliding window approach in time series clustering of intracranial pressure for patients with traumatic brain injury, In: J. Maňka, M. Tyšler, V. Witkovský, I. Frollo, (eds), MEASUREMENT 2017, Proc. of the 11th Int. Conf. on Measurement, Smolenice, Slovakia, May 29-31, 2017, s.47-50. Institute of Measurement Science, Slovak Academy of Sciences, Bratislava, ISBN 978–80–972629–0–
- VALENTÍN, K. – BAJLA, I. – TEPLAN, M.: Prediction of intracranial pressure values of traumatic brain injured patients using Hierarchical Temporal Memory network. In: J. Maňka, M. Tyšler, V. Witkovský, I. Frollo, (eds), MEASUREMENT 2015, Proc. of the 10th Int. Conf. on Measurement, Smolenice, Slovakia, May 25-28, 2015, s.59-62. Institute of Measurement Science, Slovak Academy of Sciences, Bratislava, ISBN 978–80–969672–9–
- TEPLAN, M. – BAJLA, I. – ROSIPAL, R. – RUSNÁK, M.: Intracranial pressure of patients after severe traumatic brain injury: a pilot study for lethality estimation from time series, Proceedings from 6th International Conference on Biomedical Engineering YBERC, Bratislava, Slovakia, July 2-4, 2014, 89-92, ISBN 978–80–971697–0–
 Contacts
Contacts Intranet
Intranet SK
SK