Investigators: E. Schulz, A. Stankewitz, V. Witkovsky, A.M. Winkler, I. Tracey
One of the main objectives in pain research is to seek and clarify mechanisms to alleviate suffering. In cooperation with our partners, an experiment aimed at investigating the effectiveness of cognitive strategies for the attenuation of pain was conducted. Using the 7T fMRI, the effect of three strategies on pain control in healthy individuals was investigated: (a) non-imaginal distraction by counting backwards in steps of seven; (b) imaginal distraction by imagining a safe place; and (c) reinterpretation ofthe pain valence (reappraisal). Based on the results of statistical analysis of measured data, by using the algorithms we created in MATLAB (HPMIXED – The High Performance Mixed Effects Model Toolbox), we were able to reveal typical changes in cortical brain activity for the cognitive strategies considered. A follow-up study revealed increased whole brain connectivity underpins cognitive strategies that attenuate pain. An important aspect of our research is the observed variability. We have found that each subject exhibits an individual degree of brain modulation. We show that a small decrease in brain activity in one subject may be as effective in altering perception and behavior as a large decrease in brain activity in another subject.
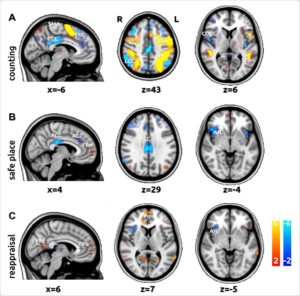
Fig. 1: Demonstration of cortical activity change at one trial level for three strategies of cognitive intervention (A-C).
Foreign partners:
- Department of Neurology, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, Munich, Germany
- Wellcome Center for Integrative Neuroimaging, FMRIB, Nuffield Department of Clinical Neurosciences, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK
Related projects: no formal project cooperation yet, indirect link with the project VEGA 2/0054/18
References:
[4] SCHULZ, E. – STANKEWITZ, A. – WITKOVSKÝ, Viktor – WINKLER, A.M. – TRACEY, I. Strategy-dependent modulation of cortical pain circuits for the attenuation of pain. In Cortex, 2019, vol. 113, p. 255-266. ISSN 0010-9452. (4.275-IF2018) Q1.
[5] SCHULZ, E. – STANKEWITZ, A. – WINKLER, A.M. – IRVING, S. – WITKOVSKÝ, Viktor TRACEY, I. Ultra-high field imaging reveals increased whole brain connectivity underpins cognitive strategies that attenuate pain. bioRxiv, 2019, DOI: 10.1101/802306.
[6] WITKOVSKÝ, Viktor. HPmixed – The MATLAB High Performance Mixed Effects Model Toolbox, 2019. https://github.com/witkovsky/HPmixed.
 Contacts
Contacts Intranet
Intranet SK
SK