Method for rapid and complete quantification of myocardial ATP flux using saturation transfer with dual-band quasi-adiabatic pulse
Investigators: Ladislav Valkovič, Ivan Frollo
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive all processes in living cells, such as: muscle contraction or nerve impulse propagation. Phosphorus saturation-transfer experiments can be used to quantify metabolic fluxes of ATP noninvasively. Typically, only the forward ATP synthesis flux through the creatine kinase reaction is investigated in the heart, by observing the decrease in phosphocreatine (PCr) after saturation of γ-ATP. The quantification of the opposite reaction, i.e. the total ATP utilization is currently underexplored, as it requires simultaneous saturation of inorganic phosphate (Pi) and PCr signals. Therefore, a novel quasiadiabatic radio frequency pulse was designed for the dual saturation to enable determination of total ATP utilization. The pulses were evaluated in Bloch equation simulations, compared with a conventional hard-cosine saturation sequence. Afterwards the technique was applied in perfused rat hearts at 11.7 T.
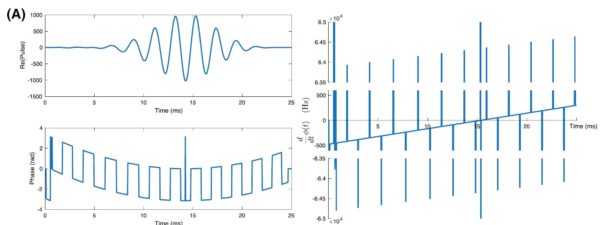
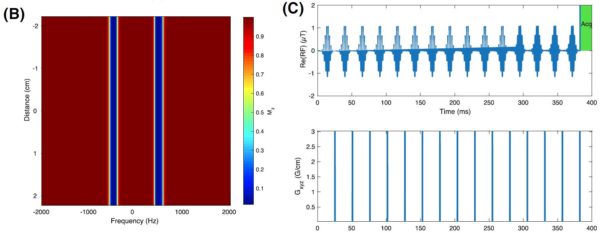
Fig. 1: The designed quasi-adiabatic optimal-control pulse, with both the real part of the pulse and its phase shown (A, top, bottom) together with the rate of change of phase (right). This shows a clear linear frequency ramp, with interleaved offsets, indicative of the adiabatic nature of the pulse. Also shown is its excitation profile as a function of space and frequency (B) expressed as the value of Mz after the pulse, showing no spectral or spatial aliasing. The pulse can then be integrated into a saturation chain followed by a hard readout (top) with gradient crushers after each excitation (bottom) as shown in (C).
Projekty: APVV-15-0029, VEGA 2/0003/20
Foreign partner: Oxford Centre for Clinical Magnetic Resonance Research, John Radcliffe Hospital, Headington, Oxford, UK
Podpísaná zmluva o vedeckej spolupráci 14. X. 2021
Publications 2021:
- MILLER, J.J. – VALKOVIČ, Ladislav – KERR, M. – TIMM, K.N. – WATSON, W.D. – LAU, J.Y.C. – TYLER, A. – RODGERS, C. – BOTTOMLEY, P.A. – HEATHER, L.C. – TYLER, D.J. Rapid, B1-insensitive, dual-band quasi-adiabatic saturation transfer with optimal control for complete quantification of myocardial ATP flux. In Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2021, vol. 85, no. 6, p. 2978-2991. ISSN 0740-3194. (4.668 – IF2020) Q1
- APPS, A. – VALKOVIČ, Ladislav – PETERZAN, M. – LAU, J.Y.C. – HUNDERTMARK, M. – CLARKE, W. – TUNNICLIFFE, E.M. – ELLIS, J. – TYLER, D.J. – NEUBAUER, S. – RIDER, O.J. – RODGERS, C.T. – SCHMID, A.I. Quantifying the effect of dobutamine stress on myocardial Pi and pH in healthy volunteers: A 31P MRS study at 7T. In Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2021, vol. 85, no. 3, p. 1147-1159. ISSN 0740-3194. (4.668 – IF2020) Q1
- MÓZES, F.E. – VALKOVIČ, Ladislav – PAVLIDES, M. – ROBSON, M.D. – TUNNICLIFFE, E.M. Hydration and glycogen affect T1 relaxation times of liver tissue. In NMR in Biomedicine, 2021, vol. 34, no. 7, e4530. ISSN 0952-3480. (4.044 – IF2020) Q1
- VALKOVIČ, Ladislav – LAU, J.Y.C. – ABDESSELAM, I. – RIDER, O.J. – FROLLO, Ivan – TYLER, D.J. – RODGERS, C.T. – MILLER, J.J.J. Effects of contrast agents on relaxation properties of 31P metabolites. In Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2021, vol. 85, no. 4, p. 1805-1813. ISSN 0740-3194. (4.668 – IF2020) Q1
 Contacts
Contacts Intranet
Intranet SK
SK